
WASHINGTON DC, Jan 16 (IPS) – We’re on the point of a technological revolution that would jumpstart productiveness, enhance international progress and lift incomes around the globe. But it might additionally substitute jobs and deepen inequality.
The fast advance of synthetic intelligence has captivated the world, inflicting each pleasure and alarm, and elevating necessary questions on its potential affect on the worldwide economic system.
The online impact is tough to foresee, as AI will ripple by way of economies in advanced methods. What we are able to say with some confidence is that we might want to provide you with a set of insurance policies to securely leverage the huge potential of AI for the good thing about humanity.
Reshaping the Nature of Work
In a new analysis, IMF employees study the potential affect of AI on the worldwide labor market. Many research have predicted the probability that jobs will likely be changed by AI. But we all know that in lots of circumstances AI is prone to complement human work. The IMF evaluation captures each these forces.

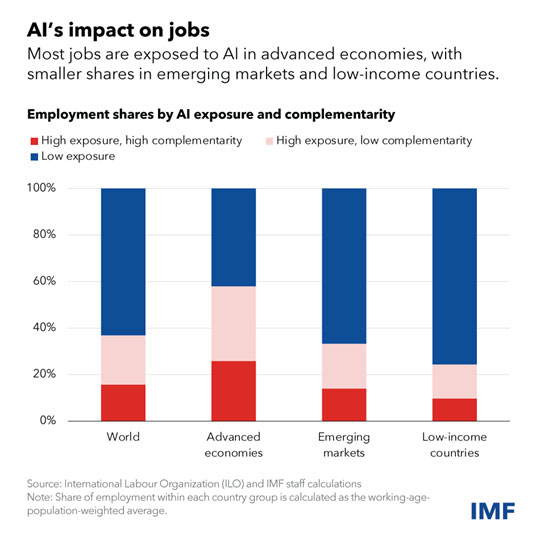
The findings are hanging: nearly 40 p.c of world employment is uncovered to AI. Traditionally, automation and knowledge know-how have tended to have an effect on routine duties, however one of many issues that units AI aside is its means to affect high-skilled jobs. Consequently, superior economies face higher dangers from AI—but additionally extra alternatives to leverage its advantages—in contrast with rising market and creating economies.
In superior economies, about 60 p.c of jobs could also be impacted by AI. Roughly half the uncovered jobs could profit from AI integration, enhancing productiveness. For the opposite half, AI purposes could execute key duties at the moment carried out by people, which might decrease labor demand, resulting in decrease wages and decreased hiring. In probably the most excessive circumstances, a few of these jobs could disappear.
In rising markets and low-income nations, in contrast, AI publicity is predicted to be 40 p.c and 26 p.c, respectively. These findings recommend rising market and creating economies face fewer speedy disruptions from AI.
On the similar time, many of those nations don’t have the infrastructure or expert workforces to harness the advantages of AI, elevating the chance that over time the know-how might worsen inequality amongst nations.
AI might additionally have an effect on earnings and wealth inequality inside nations. We might even see polarization inside earnings brackets, with staff who can harness AI seeing a rise of their productiveness and wages—and those that can’t falling behind.
Research exhibits that AI might help much less skilled staff improve their productiveness extra shortly. Youthful staff could discover it simpler to use alternatives, whereas older staff might wrestle to adapt.
The impact on labor earnings will largely depend upon the extent to which AI will complement high-income staff. If AI considerably enhances higher-income staff, it could result in a disproportionate enhance of their labor earnings. Furthermore, positive factors in productiveness from companies that undertake AI will possible enhance capital returns, which can additionally favor excessive earners. Each of those phenomena might exacerbate inequality.
In most eventualities, AI will possible worsen total inequality, a troubling pattern that policymakers should proactively deal with to forestall the know-how from additional stoking social tensions. It’s essential for nations to ascertain complete social security nets and supply retraining applications for susceptible staff. In doing so, we are able to make the AI transition extra inclusive, defending livelihoods and curbing inequality.
An Inclusive AI-Pushed World
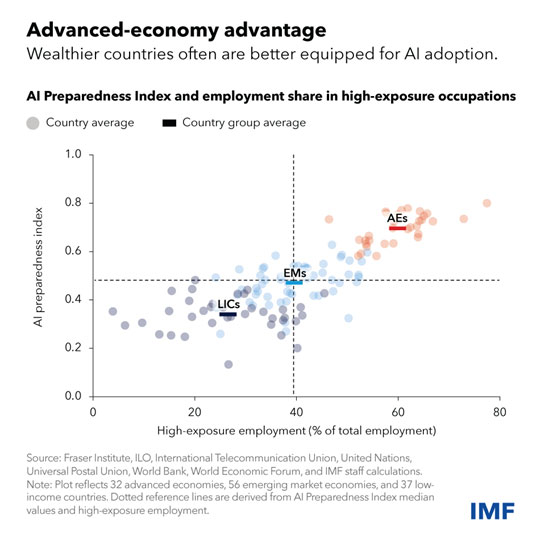
AI is being built-in into companies around the globe at outstanding pace, underscoring the necessity for policymakers to behave. To assist nations craft the suitable insurance policies, the IMF has developed an AI Preparedness Index that measures readiness in areas comparable to digital infrastructure, human-capital and labor-market insurance policies, innovation and financial integration, and regulation and ethics.
The human-capital and labor-market insurance policies part, for instance, evaluates components comparable to years of education and job-market mobility, in addition to the proportion of the inhabitants coated by social security nets. The regulation and ethics part assesses the adaptability to digital enterprise fashions of a rustic’s authorized framework and the presence of sturdy governance for efficient enforcement.
Utilizing the index, IMF employees assessed the readiness of 125 nations. The findings reveal that wealthier economies, together with superior and a few rising market economies, are usually higher geared up for AI adoption than low-income nations, although there’s appreciable variation throughout nations.
Singapore, the US and Denmark posted the very best scores on the index, based mostly on their sturdy leads to all 4 classes tracked.
Guided by the insights from the AI Preparedness Index, superior economies ought to prioritize AI innovation and integration whereas creating sturdy regulatory frameworks. This method will domesticate a protected and accountable AI surroundings, serving to keep public belief.
For rising market and creating economies, the precedence ought to be laying a powerful basis by way of investments in digital infrastructure and a digitally competent workforce.
The AI period is upon us, and it’s nonetheless inside our energy to make sure it brings prosperity for all.
Kristalina Georgieva is a Bulgarian economist serving because the twelfth managing director of the Worldwide Financial Fund, since 2019.
— For extra on synthetic intelligence and the economic system, see the December issue of Finance & Growth, the IMF’s quarterly journal.
IPS UN Bureau
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2024) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service





